Artificial Intelligence has finally crossed the chasm and gone mainstream. OpenAI’s ChatGPT, released in November 2022, took the world by storm, sparking off a AI tech race. Companies across the globe and across industries are now scrambling to figure out how to infuse AI into their products. The easy availability of the underlying AI technology means that the infusion of AI into all aspects of our lives will be quite rapid. And like all industries, healthcare too will be transformed by Artificial Intelligence. In this article, we take a look at some of the early trends and predictions regarding the usage of artificial intelligence in healthcare.
Patient Self Diagnosis and Medical Q&A
Patients typically use online search engines like Google at every step of the patient journey. Starting from trying to understand the early symptoms, researching health conditions, finding providers, decrypting medical reports, after treatment care options – Google is a constant companion at every step of that journey.
However today’s search engines fall flat at actually answering medical questions. They return back a list of 10 links and it is upto to the patient to browse through these websites and decipher what they mean. This usually leaves patients with more questions than answers.
Generative AI however is well positioned to change this. ChatGPT has proven its medical chops, passing usual medical exams with scores that far exceed the average human score. Google’s recently released Med-PALM2 has also been shown to exceed expert performance on a variety of tasks including Q&A.
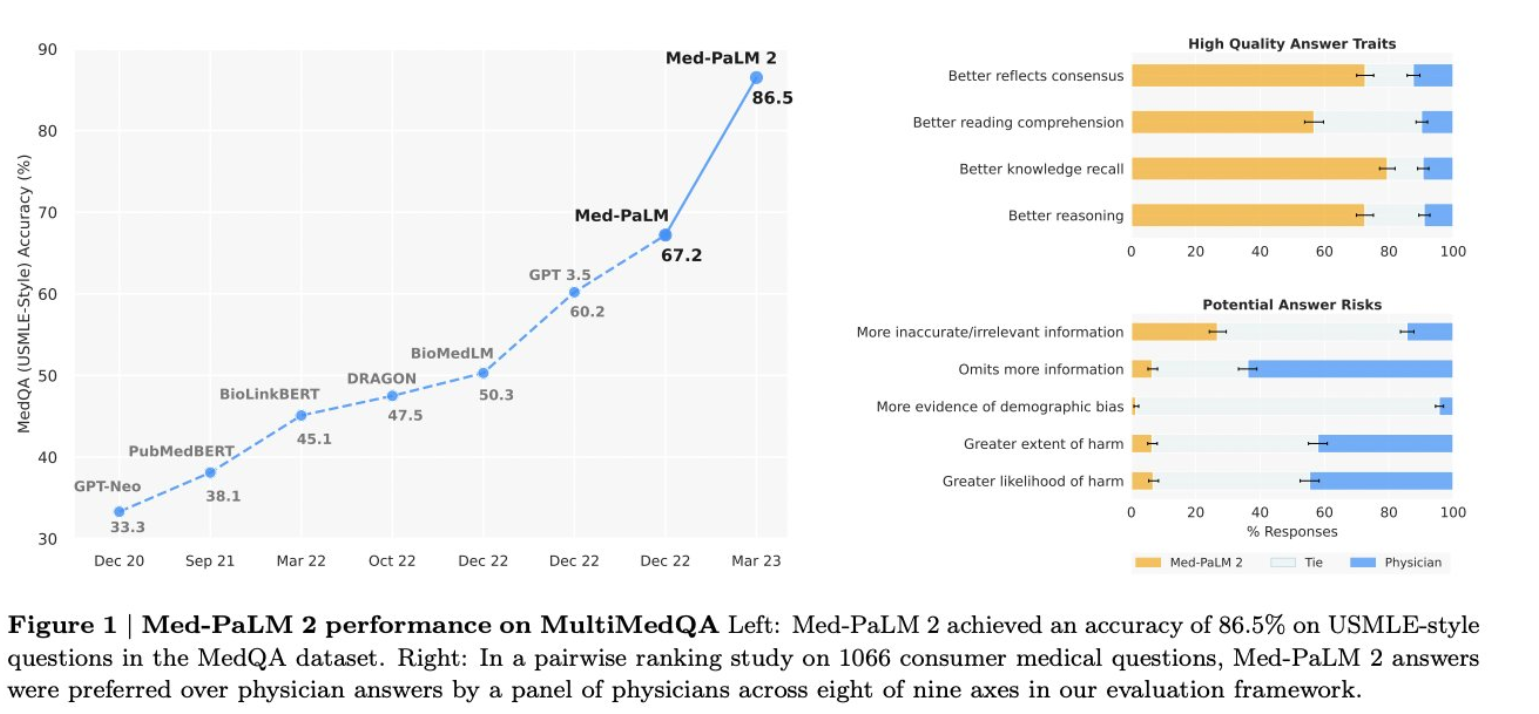
Twitter is now awash with examples of patients using ChatGPT to find answers to their questions and finding detailed answers.
The implications of this could potentially be far reaching resulting in an equitable access to healthcare across the globe. It will also have an impact on consultation volumes for simple conditions.
Personal AI Chat Bots
It is predicted that everyone at some point would have their own private chatbot which acts as their gateway to the digital world. The Joaquin Phoenix starrer ‘Her’ gives you an idea of what such a world would potentially look like. Your private chatbot would serve to handle most tasks on your behalf from booking appointments, managing your health data, reminding you to do health checkups, helping you find health data and so on. ChatBots like ChatGPT, Anthropic’s Claude, Humane are early versions of such personal AI chatbots.
What does this mean for healthcare businesses? The implications are obviously deep, but healthcare businesses will need to invest in technology that makes their systems compatible with these ChatBot technologies.
Medical Imaging & Radiology
Pattern recognition and medical imaging has always been an area where AI has made the greatest strides in the past few years. Using AI to analyse MRIs, X-Rays, Ultrasound scans are some of the areas where there are a number of successful commercialised solutions in production. At the recently concluded Google I/O 2023, Google demonstrated some exciting examples of clinicians engaging AI systems for interpreting medical images. As Medical Imaging APIs become commonly available, you can expect most EMR and Medical Imaging systems to adopt AI to assist radiologists in their tasks.
Changes in Provider Discovery
The widespread availability of ChatBots and infusion of AI into search engines will also result in a significant shift in provider discovery. Patient discovery today is driven by a combination of online searches, recommendations from friends and family and referrals. AI systems, especially personal AI Bots with deeper knowledge of a patient’s conditions and requirements, can be expected to do the heavy lifting of finding the best available provider. They will use their in-depth knowledge of the patient’s medical requirements to play matchmaker and recommend providers and services that best meet the needs.
Healthcare providers should start preparing for these changes, by developing a high quality online presence that fits into this AI driven eco-system.
AI Regulation
AI is now moving forward at breakneck speed with new breakthroughs being reported everyday with respect to both technology and its applications. Regulators around the globe and across industries are struggling to play catch up.
With respect to healthcare there are a number of key concerns:
- Healthcare Privacy: The AI race is being led by private companies and there is an increasing concern about whether these systems will be trained on confidential user data.
- Accuracy: Large Language Models (LLM) that are at the center of the current AI wave, are also prone to hallucinations – they confidently make things up and state it as a fact. In a medical context, this can be life threatening and hence using these systems safely and responsibly is a key concern for regulators.
- Bias: AI systems are also prone to bias based on their training data. So if they are trained on data which are skewed in any particular direction, they will replicate that bias in their output.
FDA Commissioner recently stated that LLM’s are “ushering in the revolution that many of us were hoping for” but the US must be “nimble in the use and regulation of large language models” to avoid being “swept up quickly by something that we hardly understand”. Europe’s AI act might consider banning open source LLMs altogether and restricting access to only licensed platforms. It will likely take some time for regulators to finalise sensible policies to regulate AI, but rest assured that regulation is definitely on the way.
A Shift Towards Telehealth
Telehealth is likely to be one beneficiary of the AI wave and is likely to result in a permanent shift towards telemedicine. The Covid driven first wave of telehealth adoption petered out post pandemic, though it settled down at a higher level. However AI is expected to drive a second wave of adoption that is likely to be patient driven. The wave will be driven by the availability of medically trained LLM’s that are capable of answering routine medical questions, coupled with AI driven improvements to personalization care, patient engagement and care availability.
From a provider perspective, it is important to start preparing for this shift. Providers should look to adopt telehealth systems that provide an integrated experience, maximize patient convenience and also incorporate multiple forms of telemedicine like video calls, remote patient monitoring and asynchronous text consultations.
Appointment Booking
Appointment Booking is a routine, repetitive task that will largely be taken over by AI systems in the future. AI Bots like ChatGPT are introducing a plugin architecture that enables these chatbots to engage with third party systems and this gives us a glimpse into how these appointment booking systems might work. Given the advantages of patient convenience and cost savings that can be realised through automation of appointment booking, it is very likely that online appointment booking systems will be one of the first patient interfaces where AI plays a big role.
Patient Notes
Providers often complain about the fatigue related to EMR usage and how this reduces the amount of time they can actually spend with a patient. AI is expected to make a big difference here. Some of the changes that can be expected to patient note taking are:
- Voice Technology: AI will be able to create a first draft of the patient notes by listening in on the patient encounter. This frees up the providers time in a big way and providers can edit the AI prepared draft as required.
- Patient History: AI will also annotate and categorize the notes and also take into account the patient’s history flagging key aspects that need the providers attention.
Epic for example is currently collaborating with Microsoft to integrate generative AI into its EMR system. Expect AI to gradually make its way into every EMR system over time.
Patient Billing
Patient Billing is another area where AI is expected to play a big role. AI powered tools will be used to simplify and expedite the processes involved in health insurance prior authorization and claims processing, for both insurance plan providers and healthcare providers. This helps enhance operational efficiency and reduces administrative burdens and costs. Google for example recently announced the introduction of their AI-enabled Claims Acceleration Suite which handles all of this.
Patient Engagement
Artificial Intelligence is also expected to revolutionise patient engagement, making it more personalized and accessible. One of the key ways will be through the creation of personalized care plans. By analyzing a patient’s medical history, lifestyle, and other relevant data, AI can tailor care plans to each individual’s unique needs and circumstances, leading to more effective treatments.
Additionally, AI-powered wearables and apps are transforming health monitoring, providing real-time data that can be used to adjust treatment plans, predict potential health issues, and offer timely interventions. This constant stream of data not only keeps patients informed about their health status but also empowers them to take an active role in their care.
Also expect to see the launch of a range of AI powered health services around consumer health devices. Apple for example is expected to be announcing a subscription service for users in June.
Summary
This article explores the transformative impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on healthcare. AI-powered tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Med-PaLM2 are revolutionising patient self-diagnosis and personal care management. AI’s role in medical imaging, provider discovery, and telehealth is also significant, improving personalization, patient engagement, and care availability. However, the rapid advancement of AI raises concerns about healthcare privacy, accuracy, and bias, necessitating careful regulation. Other areas where AI is expected to make a significant impact include appointment booking, patient notes, patient billing, and patient engagement, ultimately leading to more personalised and efficient healthcare delivery.




