Let’s first take a look at some of the major issues plaguing health providers when it comes to patient care after their clinic visit.
- Patients losing their prescriptions
- Patients not adhering to their medication
- Lack of follow-ups from patients
- Not refilling prescriptions on time
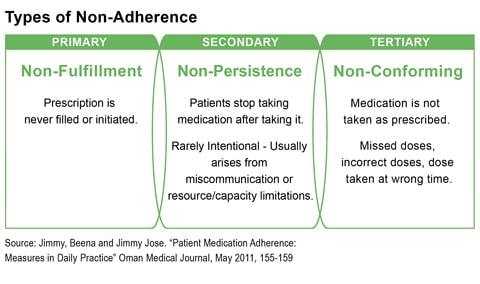
Most doctors would attest to the fact that their patients have at some point done one or all of the above. Unfortunately, this could impact their health outcomes for lack of continuity in their care, not to mention increase healthcare costs. Medication non-adherence is one of the causes for poor health outcomes. This stems from patients misunderstanding prescriptions, not having an adequate understanding of their health condition and also not following-up with their providers.
This can be a challenge for providers as health outcomes affects patient perception. While providers can hardly be blamed for non-adherence, there are ways that patients can be encouraged to follow their physician’s instructions. Technology has played a big part in ensuring better provider-patient interaction and can also help ensure better patient care through improved adherence.
E-prescriptions
It is estimated that almost 50% of patients do not adhere to their physician’s prescription, based on a WHO report. Most patients complain that they misplace their prescriptions and therefore fail to continue their treatment. Non-adherence is responsible for poor health outcomes, increased costs, and low productivity.
E-prescriptions or online prescriptions offer a suitable solution to the issue of non-adherence. Several surveys also found that patients prefer to receive e-prescriptions from their doctors. A study published in Perspectives in Health Information Management found that almost 81% of patients above 50 preferred receiving e-prescription to manage multiple prescriptions. Some of the benefits are-
- Prevents prescription drug errors
- Reduces the likelihood of lost prescriptions
- Improves medical adherence
- Reduces hospital re-admissions
- Ensures correct dosage and drug information
- Helps providers track patient fulfillment more closely
- Easier for providers to refill or alter prescriptions
- Serves as a permanent record of patient’s health history
- Improves communication with patients
- Empowers patients to be more involved in their care
Spurred on by the growth of Internet and mobile usage, e-prescriptions provide a convenient and reliable means of ensuring medication adherence.
Mobile Applications
Instant messaging and email has been used extensively for communication. This has also been the case for provider-patient communication. However, sensitive health communication requires an exclusive channel in order to respect the confidentiality of the provider-patient interaction.
mHealth applications provide suitable solutions and services to users (providers and patients), allowing them to connect, communicate and care. Real-time health solutions and services across geographical boundaries have become a reality with the arrival of health apps. Remote consultations, telehealth services, EHR and home care has now been made easier, not to mention, clinic management. Providers and health organizations can even manage their patient database, communication, appointments and revenue through clinic management applications.
Mobile applications have also helped with improving patient adherence. Mobile prescriptions, for instance, serve as reminders for medication schedules and dosage information. Much like e-prescriptions, they are more likely to be fulfilled and refilled. In addition to prescriptions, the chance of follow-up is also greater with mobile apps. Easy appointment booking, online consultations, and even telehealth services on the mobile make it easier for patients to stay in touch with their providers after clinic visits.
Patient education through the mobile is an effective means of informing patients about their care – information about their health condition, treatment plan, prognosis and latest news can be broadcasted to patients. By virtue of it being on the smartphone, a device they carry with themselves constantly, this is perhaps the most effective means of delivering informative literature. Education and awareness make patients more empowered when it comes to making healthcare decisions and also makes them more involved in their care, increasing adherence.
Electronic Health Records
Keeping track of health records and making them accessible to your patients is another way to ensure better patient adherence. Tying your EHR with e-prescriptions means that you can show patients how their health is improving with treatment or medication. Useful graphs and tables tracking patient progress are effective reinforcements for patients to stay committed to their treatment.
A complete history of medication information can be maintained by patients and providers within the EHR. This helps doctors make informed decisions and is quite useful during prescription renewal. An EHR also provides details of allergies to medication and other contraindication, which often the patient neglects to bring to their doctor’s notice. This information helps doctors avoid errors in prescribing medicines.
An online or mobile health record system, like the ContinuousCare Personal Health Record (PHR) helps patients keep track of their medication and health details, update their medication details and any additional notes that would serve as useful updates for their doctors to determine compliance and health outcomes.
Remote monitoring
Home monitoring of health conditions requires patients to generate and track their own health data. This forces them to be conscientious about their health and stay committed to their care plan. Remote monitoring of health also calls for an equal partnership between provider and patients for feedback and action. This ability to collaborate and stay connected with their providers has helped patients immensely and has reduced non-adherence.
Technology makes it possible for providers to be available to their patients remotely. For chronic care, long-term illnesses or even follow-up care, the scope of remote monitoring is truly remarkable. Provider-defined health plans can be followed by patients at home, with them providing health data from home monitoring devices like glucometers, pulse oximeters, blood pressure devices and even wearable devices. Unlike it being just about provider instructions, monitoring requires periodic updates from patients, making it an effective means of determining whether they are following their medication and complying with the prescribed treatment plan.
This is particularly relevant because studies showed that patients tend to underplay their level of non-adherence or exaggerate their level of adherence when asked about it by their doctors during clinic visits. Continuous health monitoring provides an actual account of medicine and treatment adherence, helping doctors assess patient health and improve care.
Telemedicine
Non-adherence can also be attributed to lack of communication and understanding. Studies reported that 40% to 60% of patients could not correctly recall what their physicians expected of them 10 to 80 minutes after they instructed. Yet another study reported that over 60% of the patients interviewed immediately after their doctor’s visit had misunderstood the directions regarding prescribed medications. In many cases, patients do not have a way of confirming their queries unless they visit their doctor again – a prospect many of them decide against.
Telemedicine technology and online consultations allow patients to get clarifications about their health and reduces the likelihood of them misunderstanding prescriptions. It also serves as a great way for physicians to ensure that follow-ups take place regularly, which allows them to assess and alter patient prescriptions. Telehealth solutions facilitate better patient engagement by making providers accessible to their patients more easily. A video consultation or even asking a health question is an easier alternative for patients, one that would likely help build trust in their providers and improve adherence. In the long term, continued engagement prevents prescription errors, betters patient understanding and improves outcomes of self-management.
Studies have shown that non-adherence (and consequently poor outcomes) are mostly attributed to patients being on multiple medications that they do not keep track of all their prescriptions, stopping medications when symptoms subside or even self-diagnosing their health condition. Technology has helped in breaking down the communication barrier and helped take provider-patient conversations and interactions beyond the clinic. Medication errors and prescription non-adherence can be greatly reduced with technological interventions, which seek to help demystify healthcare through better understanding.




