It is no secret that telemedicine has changed the way doctors interact with and treat patients. Despite its many advantages, the adoption of telemedicine has been slow and not without obstacles. Which therefore brings up the question – Can telemedicine be the future of healthcare delivery?

What will this mean for brick-and-mortar health organizations?
The reluctance to adopt telehealth services in hospitals and clinics has perhaps been driven by the fear that this is likely to replace in-person interaction with health providers. If patients can talk to their doctors from home, then why would they visit the clinic? A common misconception. Telehealth services like video consultations do not seek to replace normal doctor-patient interaction, particularly for first-time consultations. What it seeks to facilitate is a more convenient method of follow-up care and monitoring.
Health organizations should also see telemedicine as a means of increasing their revenue. By virtue of setting up remote consultation services by minimizing losses from no-shows. So, a patient who may not feel up to traveling to the doctor’s office can still get help by consulting via video and paying for it online. It also provides patients from other cities to get medical help that they may not have access to where they live. This means health organization can increase the reach of their care without any infrastructural costs.
Telehealth solutions, therefore, provide these businesses with limitless growth opportunity without additional overheads or resources.
What do patients feel about telehealth solutions
This is a fairly mixed reaction. While some patients are convinced that health care solutions cannot be dispensed without a physical examination, others in remote areas find it to be a boon as they would otherwise have no means to consult a specialist.
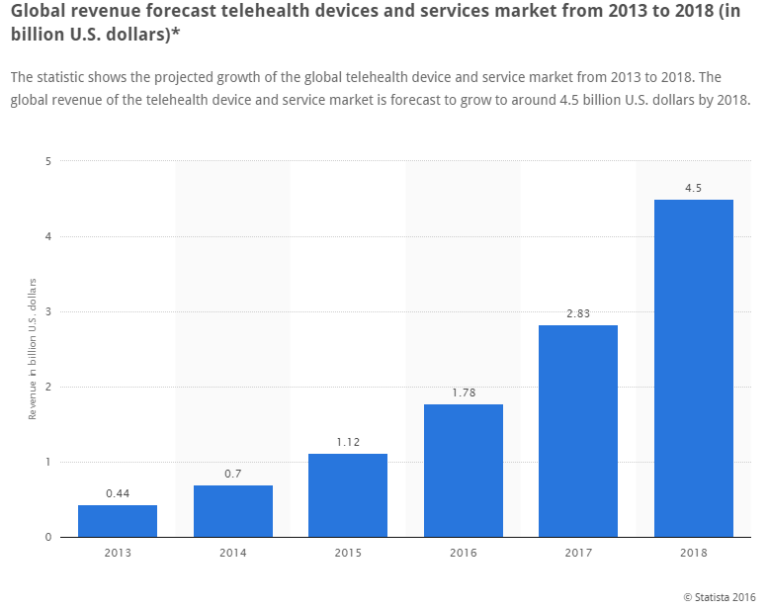
However globally, the growth in telehealth devices and services indicate that there has been a steady growth in adoption, with the market set to be valued at $4.5 billion USD by 2018. It is estimated that there are roughly 2.1 million patients using telehealth services in 2016 and this is estimated to go up to 7 million by 2018 (*Source: IHS report entitled “World Market for Telehealth – 2014 Edition.”)
This goes to show that while there may be cynicism about the quality of telehealth care, it is increasingly finding favour with users as it improves accessibility to health providers and thereby helps improve health outcomes.
Companies specializing in telehealth solutions, like American Well, MDLive, and TelaDoc, have focussed on driving doctor-patient engagement through video consultations on the web and through their mobile app. The Virtual Practice also offers video consultations tied to its Personal Health Records (PHR), thereby making it more than just a video call with your physician. Integrating consultations with health records to monitor patient progress is perhaps one of the biggest advantages of using telehealth services like the Virtual Practice.
This widespread use of telemedicine software can be attributed to growing mobile phone use and changing patient behaviour which has led to patients being constantly connected. This has been spurred on by the use of smartphones and wearable devices. The convenience it offers chronically ill patients and those living in places with limited access to specialist care is perhaps another reason why telemedicine has been adopted so readily by patients.
How is telemedicine being used by health organizations?
Telehealth services have been used for remote care. This has been particularly helpful to provide healthcare to remotely located rural areas where there is limited accessibility to health services and specialty care.
Studies by global IT company, NTT Data showed that almost 75% of patients would use telehealth services if given the option. In 2012, the number of patients who were being monitored worldwide through telehealth services was 308,000. In 2016, that number is expected to grow to 1.8 million patients. Patients being monitored through telemedicine include people with cardiovascular disease, pulmonary diseases, hypertension, diabetes and mental health, to name a few.
Physicians and health organizations agree that having telehealth solutions have made it easier to provide medical interventions when needed most. It has helped drive value-based care with a better emphasis on improving health outcomes.
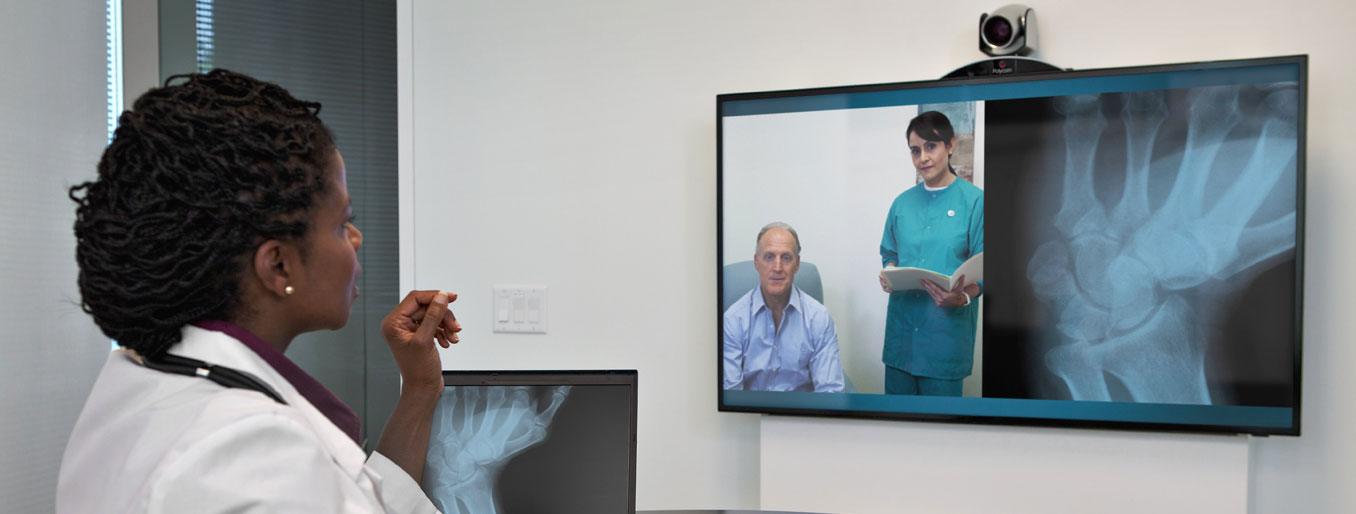
Telehealth technology is also growing by leaps and bounds. Diagnostic devices like examination camera, scopes, stethoscopes, vital signs monitors, retinal cameras and ultrasound probes have now been developed to work with telehealth systems. This provides remotely located doctors a better understanding of their patients’ condition.
With video-conferencing facilities, this software has also allowed for healthcare teams comprising of different physicians and primary care doctors to talk to each other and address clinical cases. Never before has it been this convenient for doctors to collaborate and have discussions regarding diagnostics and healthcare delivery.
While it is now being used primarily for follow-up care, it is highly likely that telemedicine is going to be the future of healthcare delivery. Being cost-effective, quick, robust and time-saving, without having to compromise on quality are some of the positives of telehealth. With better technology and intelligent software, one might also dare say that telemedicine technology could go from just being a follow-up tool to being an effective diagnostic approach.
The Virtual PracticeTM from ContinuousCare offers health providers and healthcare organizations the necessary tools to facilitate patient empowerment through patient engagement services like video consultation, telehealth services, and remote care which are tied to online health records. Learn more.




