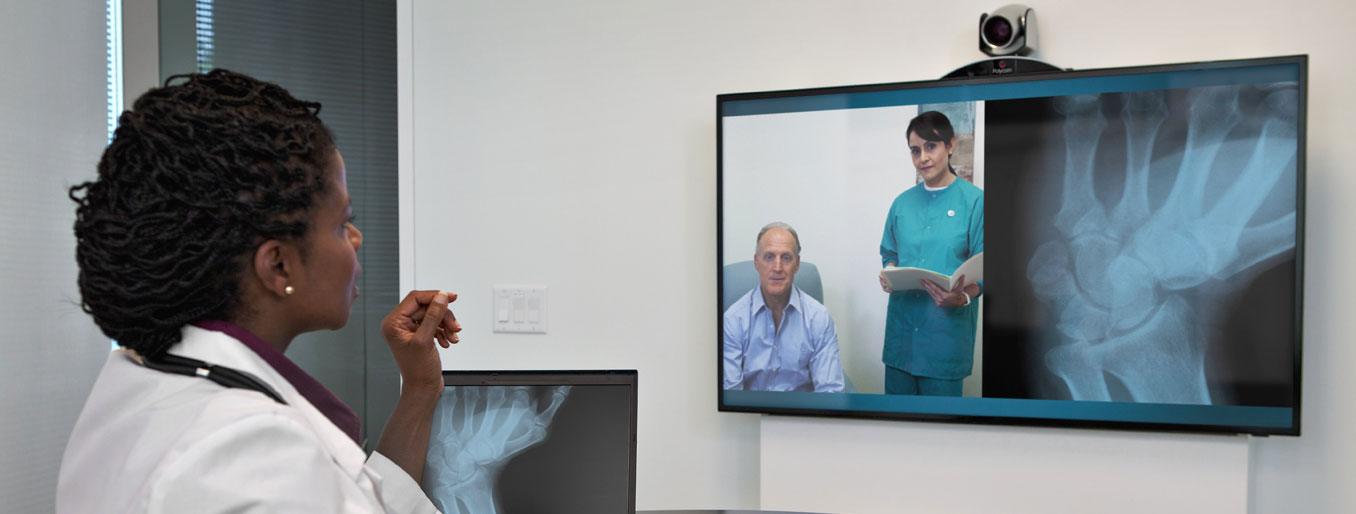
A decade ago it may have been hard to imagine health providers and patients talking to each other through their computer screens. Technology has grown by leaps and bounds, particularly in healthcare, that now, video consultations and telemedicine technology are a welcome addition to healthcare delivery.
While it may have been a novel feature for medical practices, telemedicine has the potential to increase accessibility of care, reduce healthcare costs, reduce hospital re-admissions and potentially grow businesses.
Although the possibilities seemed endless, the adoption of telemedicine technology has not been a smooth road. With regulations about practice, licensing and ethical concerns about consulting with patients remotely, health providers have grappled with several roadblocks. At its inception, the concern was whether patients would adopt this method of communicating with their providers. For providers, the question was whether a technology investment like this would reap any financial benefits.
Early adoption of telemedicine
Telehealth technology has existed for many years, being used in non-medical contexts, for research, administration and training. Its extension into medicine was initially as a collaborative care tool between health providers and health centres. Whether it was to consult on a particular case or connect rural health care centres, it was seen as a way to communicate with peers.
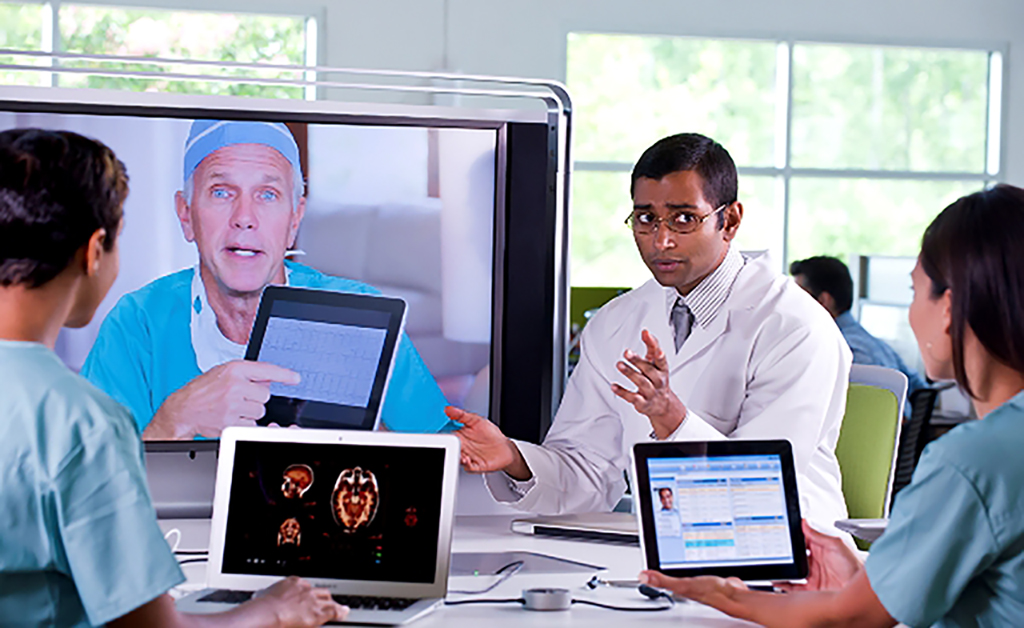

As a gradual extension of this, health centres began using specialized equipment like cameras, scopes and monitors to remotely examine patients located at a partnering care centre or rural location. Soon enough, the accessibility and convenience it offered saw it being adopted by hospitals, home-care and senior care centres and chronic care health centres. Thus opened the possibility of remote care and monitoring for a wide array of health conditions ranging from minor ailments to chronic illnesses.
However, there were still several questions surrounding the use of such technology – Is data privacy a concern? Can’t existing video calling or teleconferencing services be used for provider-patient communication?
Why telemedicine is now a must-have
Perhaps one of the reasons that telemedicine has been adopted so widely in the past few years has been the simplicity of technology, drawing from familiar behaviour using other video calling and teleconferencing applications. The only difference here is that it is health-centric, but almost mimics a face-to-face interaction with one’s patient (minus the capability to physically examine them yourself, of course).
From being a novel tech tool, telemedicine has quickly become a necessity for health providers, serving as an extension of their practice. In order to provide their patients with more value, providers have taken to ensuring continuity of care and telemedicine has enabled this.
Granted, it does have its limitations, in that it cannot be used for accurate diagnosis, or for first visits with new patients. But that is not what telemedicine is designed to be and it should not be seen as a means of replacing clinic visits completely.
What it is is a means of providing follow-up care and to some extent patient health monitoring. This is why telemedicine would be most useful in home-care centres, for chronic care management, geriatric care, mental health and even in surgery.

Telemedicine has helped in improving the reach of care to places where it was hard to come by. For instance, in the case of mental health, telepsychiatry has helped millions of patients with mental health issues who were reluctant to get help due to the stigma associated with it. Being able to provide timely intervention has helped providers get better patient adherence and health outcomes.
Considering physician shortage is a huge concern, telemedicine serves as a perfect solution to get access to specialized healthcare.
Besides the convenience for patients, providers have also begun to see the merits of telehealth technology. A recent survey conducted by a US-based telemedicine provider showed the top reasons physicians would use telemedicine in their practice –
- Concierge services for fee-paying patients
- Medication management/prescription renewal
- Minor urgent care (i.e. pink eye, fevers)
- Birth control counseling
- Home health care
- Chronic condition management
- Pediatric after-hours needs
- Behavioral health
- Post-hospital discharge
- Post-surgical follow-up
With specialized video conferencing services being developed for health communication, privacy of health data as well as confidentiality is ensured, making it a better alternative to using messaging and teleconferencing platforms.
Telemedicine continues to evolve
The future of telemedicine technology is quite promising. Patients have also embraced the practice of video consultations with their health providers. Telemedicine services on smartphones will make it even easier to connect and collaborate, making patients more active participants in their care.
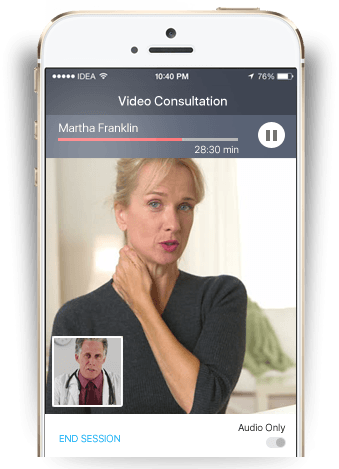
With greater emphasis on security and quality, telemedicine services also serve as a secondary source of revenue for health providers with in-built payment and invoicing functionalities. Given the wide acceptance of telemedicine, it is only a matter of time before more medical insurance companies also offer reimbursements for video consultations.
Chronic care management and enabling self-management are potentially what telemedicine will be able to support more strongly in the future. With heavy investments being made in improving the technology, health providers are driving the need for customized solutions for their practices in order to provider greater value to patient care. Given that the quality of health outcomes is closely tied to patient satisfaction, providers now understand that they stand to gain a lot from adopting telemedicine technology for their practice.
To learn about the Virtual Practice’s telemedicine services, visit https://www.continuouscare.io/features/video-consultation/. Contact us if you would like a custom solution for your business.




